|
| |
1.- SEISMOTECTONIC AND SEISMICITY (SISMOTECTÓNICA Y
SISMICIDAD)
1-01.- NEOTECTÓNICA Y TECTÓNICA
ACTIVA EN LA DEPRESIÓN PLIO-CUATERNARIA DEL SEGURA (MURCIA-ORIHUELA)
Rodríguez Estrella, T.; Hernández Enrile, J.L. y Ibargüen, J.
This work presents partial results, derived from the interpretation of
an electrical sounding array, with mechanical boreholes "log" assisted, in an
area of the Segura basin. Additionally, GIS tools have been used for slope analysis in the
valley. Results show faults presence, which give rise to Quaternary deposit layers
unevenness and geomorphic alignments in the Segura basin. These structures have been
geometrically and sometimes kinematically compared to neotectonics in the basin border.
Recent tectonic activity is inferred as a result of N140ºE and N60ºE hidden faults
reactivation. These faults are also considered as responsible for the seismicity in this
section of the Segura basin.
p.p. 53 - 63
Índice
1.02.- ESTRUCTURA SUPERFICIAL DE ANDALUCÍA Y MAR DE ALBORAN A
PARTIR DE ONDAS Rg DE CORTO PERIODO
Chourak, M; Navarro, M; Corchete, V. y Badal, J.I.
A methodology that has been applied for a relatively short time on
Seismology is the modelling of very shallow structures from the inversion of dispersion
values (group velocity of short period Rg waves). This is possible, because of the very
short period Rg wave group velocity is sensitive to the variations in the structure of
shear velocity for the shallowest layers of the crust. Indeed this shallow structure
influences of remarkable way in the level of the seismic shock, happening that in the
cases of destructive earthquakes it is observed that the phenomena of local amplification
are strongly related to the materials nonconsolidated (low shear velocity), which are
blame of important modifications in the amplitude of the seismic shock produced by these
earthquakes. This does that studies directed to the characterisation of the shallow Earth
structure are always welcome. In this line, in the present study we analysed the
dispersion of the Rg waves generated by earthquakes and blasts happened in period 1990-95
and registered by the Andalusian Geophysical Institute (IAG). These events are all local
earthquakes, that is to say, they have happened in the area under study. We have
determined the group velocity of the Rg wave fundamental mode by means of the standard
filtering techniques like MFT or TVF, applied to the registrations of these events. We
have obtained the dispersion curves for the paths source-station with a range of periods
between 0.5-6.0 s. The group velocity values are included in the range 0.60 to 2.05 km/s.
We have obtained the models of shear velocity for a range of depth between 0 to 1000 m by
means of the stochastic inversion of such dispersion curves. This range of analyzed depth
is very interesting for the studies of Seismic Engineering and the Prevention of
Seismic Disasters.
p.p. 65 - 73
Índice
1.03.- SEGMENTACIÓN TECTONICA DE LA FALLA DE ALHAMA DE MURCIA Y
ACTIVIDAD PALEOSÍSMICA ASOCIADA. CONTRIBUCIÓN A LA DETERMINACIÓN DE LA PELIGROSIDAD
SÍSMICA EN LA REGIÓN DE MURCIA
Martínez-Díaz, José J. y Hernández Enrile, José L.
Previous Alhama de Murcia Fault (FAM) segmentations, are based on
geometrical variations of structural features on fault zone (trend changes of main fault,
secondary fault density, fault zone width,...etc.). However, these features are not
present in seimogenic depths. For this reason, in this work a segmentation of FAM, founded
on criteria giving information about lateral variations of fault behaviour, not only in
shallow levels but in the whole seismogenic crust, is presented. This criteria are: A:
Main fault zone trend changes. B: Fault zone structure in depth. C: Control of fault
activity on landscape and megastructures creation. D: Linked seismicity and E:
Paleoseismic activity.
p.p. 75 - 87
Índice
1.04.- ANÁLISIS PALEOSISMOLÓGICO DE UNA FALLA SISMOGÉNICA SIN
REGISTRO HISTÓRICO: LA FALLA DE "EL CAMP" (CADENAS COSTERAS CATALANAS)
Masana, E.; Villamarín, J.A. y Santanach P.
Seismic hazard analysis in areas of long seismic cicles are not
adequate when based only on historical and instrumental seismicity. Seismicity previous to
the catalogue should be considered in these cases and this information is supplyed by
paleoseismology. The El Camp fault paleoseismicity was studied by means of a
geomorphological analysis, trench analysis and the use of diferent absolute dating methods
(14C, U/Th, termoluminiscence). Although the historical catalogue does not show
destructive earthquakes the paleoseismological analysis points out that: 1) the El Camp
fault is seismogenic, 2) displays two segments, and 3) the southern segment, wich has more
recent activity, shows evidence for two or may be three 6.5 M earthquakes after 80000
years. This implies an increment from 10-5 to 10-3 of the
probability of annual excedence of 0.2 g acceleration in the scarp area.
p.p. 89 -97
Índice
1.05.- CATÁLOGO DE TSUNAMIS EN LAS COSTAS ESPAÑOLAS
Izquierdo, A. y Tordesillas, J.M.
A tsunami catalogue has been elaborated for the Spanish coasts, both
for pre-instrumental and instrumental periods. A study and a revision of all the possible
tsunamis found through several earthquake catalogues, tsunami studies, etc. have been made
with the aim of clarifying the event descriptions -sometimes really confusing-, both for
true and false tsunamis. Catalogues and references from other countries (Portugal,
Algeria, etc.) have also been consulted. The format and the criteria applied are the same
used to elaborate the European Tsunamis Catalogue by the European working group GITEC
(Genesis and Impact of Tsunamis on the European Coasts).
p.p. 99 - 107
Índice
1.06.- CATÁLOGO DE SISMICIDAD: VOLUMEN I DEL ATLAS SÍSMICO DE
CATALUNYA
Susagna, T.; Goula, X. y Roca, A.
Since 1991, macroseismic data from North-East Spain and South of France
have been compiled with the aim of producing an homogeneous seismic catalogue useful for
reliable seismic hazard studies. This compilation has been carried out first through a
revision and critical comparison of existing catalogues, in particular those from the
Instituto Geográfico Nacional and SIRENE (France); results from recent investigations on
historical earthquakes have been incorporated to the catalogue; for the 20th century
events, the original macroseismic questionnaires have been re-analysed.
The publication of our catalogue (book and CD-ROM) corresponds to the
Volume 1 of the "Atlas Sísmic de Catalunya" which is composed of 918 individual
records, one for each event, 58 of them corresponding to fake earthquakes. Moreover, the
catalogue includes maps with the location of the epicentres and maps with distribution of
felt intensities for individual events.
p.p. 109 - 117
Índice
1.07.- UNA METODOLOGÍA PARA MEJORAR LA CONFIGURACIÓN GEOMÉTRICA
DE REDES SÍSMICAS LOCALES. APLICACIONES EN INGENIERÍA CIVIL
Lindo-Ñaupari , R.; Herraiz, M. y Vadillo, O.
According to previous studies (Lindo y Herraiz, 1995a,b; 1998), a
simple methodology aimed at analysing the performance of local seismic networks, is
described. To get this objectif, a computer program which evaluates the efficiency of this
kind of networks and estimates the contribution of every P or S phase to the hypocentral
solution, has been developed. Its application to cases previously studied, confirms the
utility of the methodology which has also been applied to real problems of natural and
reservoir-induced seismicity.
p.p. 119 - 127
Índice
1.08.- CUANTIFICACIÓN DE DEFORMACIONES RECIENTES MEDIANTE DATOS DE
NIVELACIÓN DE PRECISIÓN EN EL SUDESTE PENINSULAR
Giménez, J.; Goula, X y Suriñach, E.
Historical high precision leveling data of the Instituto Geográfico
Nacional have been used to quantify recent vertical movements in southeastern Spain. Some
movements are related to tectonic activity, thus they coincide with neotectonic faults
which, in some cases, has associated seismicity.
The main anomalies are: a step of 2 mm/year located between Villena and
Almansa (ENE-WSW faults); a step of 0.9 mm/year located between Águilas and Terreros
(NNE-SSW fault); a sinking of the Almería basin of 1.5 mm/year (NW-SE faults); two
anomalies between Huelma and Moreda (ENE-WSW faults); and a step of 1 mm/year located at
the Alborán coast (NW-SE and NE-SW faults). Distribution of the anomalies reveals that in
the external betics vertical movements are related to ENE-WSW inverse faults, and that in
the internal zone they are associated with NE-SW and NW-SE normal faults. These movements
agree with the present day regional stress tensor, which indicates an approximately N-S
compression together with an approximately E-W extension.
p.p. 129 - 138
Índice
1.09.- ESTRUCTURA ANELÁSTICA DE DOS REGIONES HERCÍNICAS DE LA
PENINSULA IBÉRICA OBTENIDAS A PARTIR DE DISTINTOS ALGORITMOS DE INVERSION
Olarte, J.; Lana, X. y Canas, J. A.
The 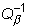 structure of two hercinian
regions of the Iberian Peninsula have been determined by means of anelastic attenuation
factors for inversion procedure that belong to trains of Rayleigh superficial waves
obteined of the ILIHA project. At present, we apply three different inversion algorithms
(stochastic, total and simulated annealing) to the simple and joint inversion of the phase
and group velocities and factor attenuation anelastic for Rayleigh waves fundamental mode
with the aim of deducing structure of two hercinian
regions of the Iberian Peninsula have been determined by means of anelastic attenuation
factors for inversion procedure that belong to trains of Rayleigh superficial waves
obteined of the ILIHA project. At present, we apply three different inversion algorithms
(stochastic, total and simulated annealing) to the simple and joint inversion of the phase
and group velocities and factor attenuation anelastic for Rayleigh waves fundamental mode
with the aim of deducing 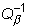 structures of the
Peninsula. The values of structures of the
Peninsula. The values of 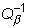 are low between depths of
0 and 250 km and the astenosfera is detected between 80 and 180 km, in agreement with
results of dispersion properties of Rayleigh waves. are low between depths of
0 and 250 km and the astenosfera is detected between 80 and 180 km, in agreement with
results of dispersion properties of Rayleigh waves.
p.p. 139 - 148
Índice
2.- SEISMIC HAZARD (PELIGROSIDAD SÍSMICA)
2.01.- SISMICIDAD EN LA REGIÓN
DE MURCIA DURANTE EL QUINQUENIO 1994-1998
Ibargüen Soler, José y Rodríguez Estrela, Tomás
The english abstract and the o.v. paper will be included after the end
of the Congress, like addendum to first volume of the Proceedings.
pp. 151
Índice
2.02.- La tasa de desplazamiento de una falla como aproximación de
primer orden en las estimaciones de peligrosidad sísmica
Villamor, P. y Berryman, K.R.
Paleoseimic techniques, particularly fault trenching, are increasingly
used in seismic hazard studies in low seismicity (so-called intraplate) regions. However,
applying techniques that were originally developed in high seismicity regions is
difficult. In contrast to high seismicity regions, there are low rates of landscape
change, weak geomorphic expression of fault activity, and difficult-to-date Pleistocene
deposits in low seismicity regions. The application of paleoseismic techniques to derive a
full range of fault rupture parameters is therefore very difficult.
In this paper we illustrate the utility of a single parameter - fault
slip rate - as a first approximation to the hazard posed by large earthquakes that result
in surface faulting. Fault slip rate is the most-easily obtained parameter because it may
be derived simply from displacement and the age of the offset unit whether it be
stratigraphic or geomorphic. Long-term slip rates can often be obtained from traditional
geological mapping, which is commonly already developed to a high standard in low
seismicity and intraplate regions. We suggest that because fault slip rate is highly
correlated with fault rupture recurrence, this provides a ready basis for preliminary
hazard evaluation and also a criteria for assessing priorities for more detailed study.
p.p. 153 - 163
Índice
2.03.- REVISIÓN DE MODELOS DE MOVIMIENTO FUERTE DEL SUELO Y
APLICACIÓN A LA PREDICCIÓN DE ESPECTROS DE RESPUESTA
Benito, B; Cabañas, L.; López, M.; Jiménez, M.E. y
López-Arroyo, A.
In this work a practical application of a methodology for specific
response assesment in a certain site, is developed and carried out according to the state
of the art. For that purpose, in a first stage the strong motion models proposed in the
literature are revised, and, the main characteristics defining their application are
extracted: source area data, scales, magnitude and distance ranges, and, site
classifications adopted. These models are applied to a certain site, for that reason a
hazard analysis of it is fulfilled previously, establishing scenarios characterized by
certain magnitude-distance pairs. These are introduced in the aforementioned models and
the corresponding espectra are predicted, which are finally compared with those
established by different normatives.
p.p. 165 - 175
Índice
2.04.- Predicción espectral DE LA ACCIÓN SÍSMICA a partir del
Modelo de Brune modificado
Catalán, A.; Roca, A. y Goula, X.
It is proposed a semiempirical model for predicting earthquake spectra
(FSA, PSV) on rock trough a modification of the well known Brune’s model by
introducing a stress drop, D s , and
a maximum frequency, fmáx, both of them variable. All the parameters involved
in the model are related to a single parameter, the seismic moment, M0 (or
magnitude), in addition to the epicentral distance. A regression analysis for obtaining
the dependence of D s and fmáx
on M0 has been carried out using data available from different seismic
areas. The corner and maximum frequencies, which control the shape of the spectrum, are
then obtained. The model is applied to a set of accelerograms from the SMART-1 array in
Taiwan. In spite of the fact that seismic moment values for this events are not available,
if these M0 values are deducted from homogeneous determinations of magnitude
then there is a good agreement with the values predicted by the proposed model.
p.p. 177 - 189
Índice
2.05.- CREACIÓN DE UNA BASE DE DATOS SOBRE DAÑOS SiSMICOS EN
EDIFICACIONES
Feriche, M.; Esquivel, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.; Esteban, M.J.; Garrido,
M.J.
To evaluate the degree of damages suffered in constructions caused by
earthquakes of moderated to strong, we need of the managing of a considerable photographic
documentation. This institution elaborates a data base that provides images and data
several: parameters of the earthquake, location, number of victims, etc.; that they
provide additional information on the earthquake referred in each photo. This data base
will facilitate the rapid managing of documentacion and information in addition to their
several clasification.
p.p. 1191 - 195
Índice
2.06.- BANCO DE DATOS DE MOVIMIENTO FUERTE DEL SUELO
"MSF" DESARROLLADO EN EL PROYECTO DAÑOS
Cabañas, L.; Benito, B.; Cabañas, C.; Jiménez, M.E.; Gómez,
P.; López, M.; Álvarez, S.; Ramírez, M.S. y Nuche, R.
One of the main activities developed in Daños Project has been the
design of a strong motion databank, compiling and classifying accelerograms and spectra
from all over the world. This databank is complemented with an associate database where
the available seismic information corresponding to the records is catalogued, and, with a
developed software for: consulting purposes, record processing, graphic representation and
derived parameter assesment. In this work the characteristics of the developed databank
and database are presented, emphasizing in aspects such as its composition, the
information structure, possible exploitations, and so forth. The adopted design makes
easier the selection of the records and parameters for its analysis and treatment, and
later applications in the Earthquake Engineering field.
p.p. 197 - 205
Índice
2.07.- ANÁLISIS PROBABILISTA DE LA PELIGROSIDAD SÍSMICA
Sánchez Cabañero, J.G. y Jiménez Juan, A.
The modern Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Análisis (PSHA) is a
probabilistic methodology used to estimate the likelihood of exceeding the ground motion
caused by earthquakes at a given site or terriory in a given future time. Due to large
uncertainties associates with the geosciences data and with their modeling, multiple model
and/or expert interpretations are often always possible, included at high seismicity
areas. This lead disagreement among results of different analysis, which in the current
time, like in the past, has transfered this contend to regulatory arena. In order to
update the method in accordance with the present state-of-the-art, and to improve
stability and clearness on the PSHA process and results at US, the Nuclear Regulatory
Commission, the Department of Energy and the Electric Power Research Institute,
co-sponsored a proyect to provide guidance on how to perform a PSHA, of which we show in
this paper his philosofy and a very brief method overview, in order to look for
institutions and people co-operation to promote his use in Spain.
p.p. 207 - 225
Índice
2.08.- APLICACIÓN DE LOS
FRACTALES AL ANÁLISIS DE LA DISTRIBUCIÓN DE SISMOS EN EL ÁREA IBERO-MAGREBÍ
Gumiel, Pablo
Fractal analysis techniques have been applied to the earthquakes
distribution in the Ibero-Maghrebian Region. The relationships between the number of
earthquakes and their magnitude, during three periods of time: 20 years (1977 - 1997), 10
years (1987 - 1997) and 5 years (1992 - 1997) have been studied, using the seismic records
catalogue of the IGN. It has been proven that the Gutenberg & Richter equation, for
earthquakes with magnitude between 3 and 7 in the Richter scale is scale-invariant (power
law). But the instrumental earthquakes with magnitude (mg<3) do not show the same
scaling properties. The seismogenic processes are not strictly fractals, they do not
preserve self-similarity, and therefore should be anisotropic fractoids, and their
dimension of tensorial nature, and can be considered as multifractal systems.
Nevertheless, the global seismicity in the zone is statistically fractal, or is organized
following fractal laws.
p.p. 227 - 237
Índice
3.- SEISMIC ZONATION (ZONACIÓN SÍSMICA)
3.01.- MAPAS DE PELIGROSIDAD Y VULNERABILIDAD SÍSMICA A ESCALA
1:5000 DE LA CIUDAD DE MURCIA
Mulas, J.; Fresno, F.; González de Vallejo, L. y López Arroyo,
A.
The basic
(local amplification factors) and final (seismic hazard and vulnerability) mapping for the
seismic microzonation of Murcia city, at scale 1/5000, have been developed from a
methodology with an indirect and semiempiric character, following, when possible, the
nowadays manuals and guides (TC-4, APFS, ATC, etc.). The main starting point has been the
processing of the particular data and characteristics (geotechnical, hydrogeological,
construction, etc) for the establishment of the seismic response models in each of the
zones, checking with similar cases in the world. The final cartographical documents are
focussed to a direct utility in the urbanistic planning (general plans, construction
rules, etc) and the civil protection (emergency plans).
p.p. 241 - 250
Índice
3.02.- MAPA DE ZONAS SÍSMICAS DE CATALUÑA
Secanell, R.; Goula, X.; Susagna, T.; Fleta, J.; Roca, A.
In order to evaluate the seismic hazard in Catalonia a new earthquake
catalogue and a new seismic zonation have been used. Seismic data have been adjusted to
three occurrence models: a doubly truncated distribution of Gutenberg-Richter, a model of
extreme values (Gumbel I and III), and a poissonian non-stationary model. After verifying
the quasi-stationary character of the seismic catalogue, the evaluation of seismic hazard
has been carried out through a probabilistic model and a deterministic model in terms of
macroseismic intensity. The accuracy of the seismic hazard probabilistic evaluation has
been estimated by means of a Montecarlo sensitivity analysis. It is presented a map of
seismic zones obtained from a joint probabilistic and deterministic process for mean soil
condition. Finally soil effects are considered at a regional scale.
p.p. 251 - 259
Índice
3.03.- MICROZONACIÓN SÍSMICA DE LA CIUDAD DE ALMERÍA
Navarro Bernal, M.;
The english abstract and the o.v. paper will be included at the end of
the Congress, like addendum to Proceedings.
p.p. 261
Índice
3.04.- ZONACIÓN SÍSMICA DE LA CIUDAD DE BARCELONA
Cid, J.; Figueras, S.; Fleta, J.; Goula, X.; Susagna, T. y
Amieiro, C.
The city of Barcelona from 1995 is being object of several studies for
the evaluation of their seismic risk, participating diverse investigating institutions; in
particular we present the seismic zonation of the city based on the seismic response of
the soil. The principal parts of the city are built on a Quaternary covert that yields on
a Paleozoic or Tertiary basement depending on the sector, and that could produce possible
seismic amplifications. The seismic response of the subsoil of the city of Barcelona has
been simulated numerically in 70 points, using Shake'91, a one-dimensional
lineal-equivalent method. A process of Montecarlo has been integrated with the objective
to analyse the associated uncertainties. In the proposed seismic zonation of the city of
Barcelona three zones are classified taking into account the kind of Pleistocen or Holocen
outcrop and the kind of Paleozoic or Tertiary basement.
p.p. 263 - 271
Índice
3.05.- MICROZONIFICACIÓN SÍSMICA DE BARCELONA UTILIZANDO EL
METODO DE NAKAMURA. VENTAJAS Y LIMITACIONES
Alfaro, A.; Navarro M.; Sánchez J.; Pujades, L.G.
Among the different techniques used with microtremors for seismic
microzonation, the Nakamura’s method has been one of great acceptance due to the easy
use at field as well as in the data processing. It has been used in many cities with
different geotechnical characteristics. Also, it has been proven at some cities that
Nakamura’s results agree with those of laboratory tests or with earthquake analysis
and numerical models, nevertheless it has not been the same at all sites. In the city of
Barcelona, where the task of seismic microzonation has recorded more than 350 microtremors
at 204 different sites, a critical analysis on the results is done.
p.p. 273 - 278
Índice
3.06.- Calibración de métodos de modelización de efectos
locales: Euroseistest (Grecia)
Figueras, S.; Cid, J.; Goula, X.; Susagna, T. y Roca, A.
With the purpose to calibrate different ground motion prediction
methodologies for the site effects analysis, "blind" experiments are organised
in the last years in various countries. We present the results obtained in our
participation in the benchmark experiment proposed in the European Community project:
Euroseistest-Euroseismod to predict the ground motion observed at the Volvi’s Valley
(Thessaloniki). 1D linear, 1D equivalent linear and 2D linear methods had been applied.
For the exercise a geological and geotechnical structural model and records in rock site
corresponding to different earthquakes were available. The ground motion in different soil
sites of the valley are predicted with the application of different numerical simulation
methods and the results are compared with the actual records.
p.p. 279 - 287
Índice
4.- PREVENTION AND CIVIL PROTECTION
(PREVENCIÓN-PROTECCIÓN CIVIL)
4.01.- RED ACELEROGRÁFICA DEL INSTITUTO GEOGRÁFICO NACIONAL. DIEZ
AÑOS DE REGISTROS
Carreño, E.; Suárez, A.; Tordesillas, J.M. y Sánchez, M.
Since 1989, the National Geographic Institute of Spain (IGN) is
installing its 3 components digital strong motion stations network. Although strong motion
stations are located mainly in cities with high or medium seismicity, some of them are
situated in cities with low seismicity, in order to obtain records in a wider area. The
target level is adjusted to the site seismicity. At present, the network has seventy
digital three components. Resolution is 12 bits (50 stations) and 18 bits (20 stations).
Ten of the 18 bits stations are dial-up and GPS time system. The available information
recorded in this period have been included in a CD-ROM database.
p.p. 291 - 298
Índice
4.02.- ESCENARIOS DE DAÑOS SÍSMICOS EN CATALUÑA
Chávez, J.; Goula, X.; Roca, A.; Mañá, F.; Presmanes, J.A.;
López-Arroyo, A.
Damage scenarios for each municipality of Catalonia are shown. The
seismic hazard input used in this estimation is the macroseismic intensity assigned to
towns in the seismic zone map of Catalonia. Another scenario for all the region is carried
out taking into account the focal data of an earthquake that took place in the
Ripollès (Eastern Pyrenees) in 1428. The methodology utilized in these computations
is summarized in four steps: a) classification of dwelling buildings in vulnerability
classes according to EMS-92; b) estimation of physical damage to buildings by means of the
damage probability matrices obtained for this scale; c) estimation of damage to people;
and d) estimation of economical losses.
p.p. 299 - 307
Índice
4.03.- CARACTERISTICAS DE LOS RIESGOS DEBIDOS A TERREMOTOS EN EL
MUNICIPIO DE ALBOLOTE (GRANADA)
Vidal, Ramses; Vidal, Francisco y Feriche, M.
The small 1956 Albolote earthquake (magnitude 5.0) caused a high
percentage of damaged constructions in this town showing the importance of site conditions
and vulnerability features in damage distribution. In order to assist local civil defense
authorities in planning the response to future earthquakes an earthquake damage scenario
mathodology has been applied. An evaluation of ground shaking distribution, buildings and
lifelines vulnerability maps, demographic analysis, structural damage maps applying the
EMS scale average damage values and finally a study of casualties for different
hypothetical earthquakes, shape this work.
p.p. 309 - 319
Índice
4.04.- ANÁLISIS DE RIESGO SÍSMICO
DEL PLAN ESPECÍFICO DE EMERGENCIA MUNICIPAL DE BARCELONA
Amieiro, C. y Cid, J.
The city of Barcelona is considered to be a moderate seismic activity
and it is classified with an intensity MSK VI for a return period of 500 years by the
Spanish Seismic Norm (NCSE-94, 1995). From 1995 it is object of several studies in order
to evaluate their seismic risk, with the finality of elaborating the Specific Plan of
Municipal Emergency for the Seismic Risk (P.E.E.M.). In 1997 an agreement of collaboration
with several institutions for the evaluation of the seismic risk in the city is made. As a
result of this collaboration and other specific studies in charge by the city council of
Barcelona, the analysis of seismic risk of the city is presented, it is the base to
elaborate the plan.
p.p. 321 - 330
Índice
4.05.- PROTECCIÓN FINANCIERA PARA DAÑOS DE ORIGEN SÍSMICO
Navas, José Mª
There is the possibility of reaching an efficient and economic
financial coverage for the damages produced by earthquakes both through private
underwriters and the public corporation named "Consorcio de Compensación de
Seguros". This paper contains a description of both the private insurance cover and
the characteristics of the cover issued by the "Consorcio", as well as the rates
applicable.
p.p. 333 - 338
Índice
4.06.- ANÁLISIS DEL COSTO DE LAS ESTRUCTURAS, ANTES Y DESPUÉS DE
LA ENTRADA EN VIGOR DE LA NCSE-94: ESTUDIO COMPARATIVO DE VARIOS CASOS PRÁCTICOS
Hernández Cortés, E.; Vallecillo Capilla, A. y Osuna Barrero,
J.M.
The principal objective of this motion is to evaluate the economic
increase that it has supposed the modifications introduced by the NCSE-94 in the design,
calculation and constructive manners in works of construction. To accomplish the study we
have split of the calculation of 23 works located in three cities with seismic calculation
acceleration oscillating between 0.11 and 0.24. We accomplish a percentual costs estimate
the obtained results generalizing them for other structures. With this analysis we intend
to centralize the investigation projects on behalf of obtaining structures with a better
seismic behavior, without supposes a overcost.
p.p. 339 - 347
Índice
4.07.- CONTROL DE VIBRACIONES EN EL ENTORNO DE LAS CUEVAS DE
ALTAMIRA
Sánchez Alciturri, J.M. y Sagaseta, C.
The new Museum and National Research
Centre of Altamira is being constructed in Cantabria (Spain) near the caves. The Altamira
caves, famous by their Palaeolithic rock paintings, are karstic cavities, known as the
"Sixtin Chapel of Palaeolithic art". Vibrations produced by the works have been
limited in order to avoid any perceptible effect on the caves and paintings. To control
this absence of effects, a continuous monitoring system has been installed. This paper
presents the monitoring system, methods developed to state the origin of any vibration
detected, and the decision method to be applied when vibrations higher than previously
stated limits coming from the construction area reach the caves. Also, conclusions about
transmission of vibrations across the stratified calcarenite where the caves have
developed are presented.
p.p. 349 - 356
Índice
4.08.- creacion de un "sitio web" de recursos dedicados a
la investigación en sismicidad histórica
Martínez-Guevara, Juan- B. y Saura, Santiago.
Key word: Information system, historical seismology, earthquake,
Internet, exchange net
They are exposed the followed steps and the structure of an information
system in Internet, of a resources Web devoted to the investigation in seismology, with
special interest in the historical seismology. The elements of this system are an internal
search motor, a publication area, download files , links to maps servers, links to sites
devoted to the seismology and other auxiliary sciences, and finally a distribution list
and three types of forums as participation. It is offered a site organized with links to
other places with thematic similar. In http://www.galbis.org/pub/aeis99.html
adresse, we can download this paper in full form.
p.p. 357 - 363
Índice
5.- REGULATIONS (NORMATIVA)
5.01.- Nueva normativa sobre
criterios sísmicos, geológicos e ingenieriles en el emplazamiento de cc. nn.
Sánchez Cabañero, J.G. y Jiménez Juan, A.
New criteria relating to seismic siting were published at EE. UU. like
a Code of Federal Regulations at January 1, 1997. This paper summarizes the most relevant
changes, wich are included in a news paragraph 50.54 (ff) and Appendix S to Part 50; in a
new Subpart B to Part 100 (paragraph 100.23); and new guides or procedures published at
March 30, 1997. The three major objetives from proposed changes are following: to update
and clarify the existing seismic and geological requirements in Appendix A to Part 100; to
revise seismic site criteria to reflect current understanding and advancements in the
geosciences and earthquake engineering, like Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analisis
methodology or like digital instrumentation to suport seismic criteria relates with the
plant operation with safety; and to provide a flexible structure to easy permit future
considerations of new technical understandings. The current experience has show these
proposed criteria as key to protecting public health and safety. Because the EE. UU.
Regulations are considered to NPP Spanish licensing process, it will be useful and with
benefit to implement and develop the new siting criteria in the nuclear Spanish sites.
p.p. 367 - 374
Índice
5.02.- cOMPARACIÓN DE LA FIABILIDAD ESTRUCTURAL RESULTANTE AL
APLICAR DISTINTAS NORMATIVAS EN EL CAMPO DE LA INGENIERÍA CIVIL Y DE INSTALACIONES
INDUSTRIALES
Ordoñez Villalobos, Arturo
The english abstract and the o.v. paper will be included at the end of
the Congress, like addendum to Proceedings.
p.p. 375
Índice
5.03.- EL MÉTODO DE LOS
ELEMENTOS FINITOS PARA EL ANÁLISIS SÍSMICO DE ESTRUCTURAS CONFORME A LA NORMA ESPAÑOLA
NCSE94 Y EUROCÓDIGO 8
Moreno Fernández de Yepes, Miguel Ángel y Lancha Fernández,
Juan Carlos
Since 1974, in which the seism-resistant code P.D.S. 1 was published,
the knowledge on seismology and seismic engineering has significantly progressed. All this
progresses have been gathered together. Therefore in 1994, the new seismic code NCSE-94
was adopted and recently the Eurocode Nº 8 has appeared. Simultaneously to this
scientific and normative advance, during these 25 years the computing programs as well as
the computers have radically evolved. Nowadays we can count on more accurate and
sophisticate computing methods that make possible to perform analysis that were
unthinkable few years ago. This article will try to show the nowadays available different
computing methods in the structure seismic design as well as tools that make this analysis
possible.
p.p. 377 - 381
Índice
5.04.- Nuevas aportaciones para el calculo de la atenuacion SISMICA
en la zona de Azores-Gibraltar. Implicaciones en la actual Norma Sismorresistente
Martínez Solares, J.M. y López Arroyo, A.
A large amount of macroseismic information obtained in Spain on
occasión of two large earthquakes located in the Azores-Gibraltar zone, occurred in 1755
and 1969, that has not been analyzed till now recommend a new consideration of the
attenuation law previously obtained for seismicity from the area. The present work
describes the analysis carried out of such information, which result in an intensity
attenuation law that differs significantly from the one used for obtained the hazard map
included in the Spanish Code NCSE-94; this result suggests that the seismic action
considered in the analysis of structures to be built in that zone should be modified.
p.p. 383 - 391
Índice
6.- SOIL DYNAMICS (DINÁMICA DE SUELOS)
6.01.- EVALUACION DE LA RESPUESTA SISMICA DEL SUELO POR EL METODO
"REFERENCE SPECTRAL RATIO" Y SU APLICACION EN LAS PLAYAS DE SUDÁFRICA
Fernández Julián, L.M. y Brandt, M.B.C.
The site response of different places of the City of Durban in South
Africa has been evaluated using a refined version of the Nakamura’s Method (spectral
ratio, H/V of the seismic noise). The new version uses the spectral ratio obtained at a
hard rock site as a reference to evaluate the seismic amplification of softer sites.
The seismic response of the site is presented in terms of the
amplification factors versus frequency and in relation to the hard rock reference site.
The method is of easy implementation, even in the midst of noisy urban areas. The results
are stable and independent of the noise. It is recommended its use in seismic zonification
projects.
p.p. 395 - 404
Índice
6.02.- EVALUACIÓN ANALÍTICA DEL POTENCIAL DE LICUEFACCIÓN
Martínez, Francisco; Martí, Joaquín y Simic, Davor
A methodology is described for predicting the possible development of
ground liquefaction. The calculation of the foreseeable pore pressures is based only on
borehole data. The calculation have been carried out with ABAQUS/Standard, a general
purpose finite element package. They include the evaluation of the seismic demand,
described by the profile of peak shear stresses expected in the ground during the
earthquake, the determination of the corresponding pore pressure increments and their
dissipation within the ground. The comparison of the calculated pore pressures with the
existing effective pressures allows estimating the liquefaction potential of the soil
profile considered.
p.p. 405 - 415
Índice
6.03.- UNA TÉCNICA NUMÉRICA PARA LA DETERMINACIÓN DE RIGIDECES
DINÁMICAS DE CIMENTACIONES SOBRE SUELOS SATURADOS
Aznáres, J.; Maeso, O. Y Chirino, F.
A three-dimensional Boundary Element model for computation of dynamic
stiffnesses of foundations resting on fluid-filled poroelastic soils is presented. The
dynamic behavior of the porous medium is represented according to Biot´s theory.
Foundations are assumed to be rigid and massless. The contact conditions can be pervious
or impervious. The technique is applied to thecomputation of dynamic stiffnesses of
foundations resting on a poroelastic half-space or an a poroelastic stratum based on a
rigid or compliant base. The model presented is able to represent more general cases than
do the existing approaches.
p.p. 417 - 425
Índice
6.04.- EL MÉTODO DE LOS ELEMENTOS DE CONTORNO APLICADO A LA
CUANTIFICACIÓN DEL EFECTO LOCAL
Álvarez Rubio, S. y Alarcón, E.
Site surficial geology and topographic features modify some of the
characteristics of the seismic waves propagated from the source to the surficial layer
base: this contribution is known as the site effect. Many techniques have been developed
for the study of this effect; in this work the numeric approach called the direct boundary
element method (DBEM) is presented. Through the DBEM the tensions and amplitudes are
assesed along the discretized boundary, by solving, in the frequency domain, Somigliana`s
Identity. The results achieved by the application to 2-D models, for media with different
dinamic characteristics under significant topographic features, are tested with those
known in the literature, validating the method for site effect purposes.
p.p. 427 - 434
Índice
6.05.- DETERMINACIÓN DE
CARACTERÍSTICAS DINÁMICAS DEL SUELO A PARTIR DE MICROTEMBLORES
Alfaro, A.; Egozcue, J.J. y Ugalde, A.
The determination of static and
dynamic characteristics of soils requires expensive field and laboratory studies.
Sometimes it is necessary to formulate hypothesis about the dynamic characteristics of
soils using different models. The use of microtremors to characterize soils by period
ranges and amplification levels dates from the 50’s. The methodology proposed by
Nakamura in 1989 for the estimation of the rough system function of soils by means of the
three component microtremor recordings at the surface gives reliable results, in most
cases, for the fundamental periods of ground amplification. However, the method does not
predict accurately the amplification at the resonance frequency. In this work, the
applicability of the Nakamura’s spectral ratio method is dicussed, and some numerical
improvements from the point of view of signal processing are proposed. We also present
some examples of the application of the method and the results are compared with those
obtained by means of the traditional estimation of the system function.
p.p. 435 - 441
Índice
6.06.- ZONIFICACION SISMICA DE LA CUENCA DE ALCOY MEDIANTE UN
SISTEMA DE INFORMACION GEOGRAFICO
García Mayordomo, J.
Alcoy Basin is an important
industrial and demographic zone of the Alicante region (Spain) which has suffered
disastrous earthquakes in the past. In this work a seismic zoning of the area is
approached based on acceleration data supplied by the spanish seismo-resistive provisions
(NCSE-94), the response espectra defined in the european provisions (Eurocódigo 8) and
geological and geotechnical data managed by a Geographyc Information System (GIS). At
first soil clasification of Alcoy Basin and spacial arrangement are made. Subsequently
soil response is established and liquefaction and slope instability ocurrency are analysed
based in two hypothetical levels of seismic hazard (intermediate and high).
p.p. 443 - 450
Índice
7.- STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS (DINÁMICA DE ESTRUCTURAS)
7.01.- INFLUENCIA DE LAS ACCIONES SISMICAS SEGÚN LA NORMA NCSE-94
EN ESTRUCTURAS DE MALLAS ESPACIALES
Bayo, E.; De la Rosa, M. y Bustinza , J.
This paper presents a study on the influence of the seismic actions
imposed by the Spanish code NCSE-94 on latticed spatial structures composed of single and
double layers. In general terms, these structures are stiff in their own plane but show a
large compliance under out of plane forces such as the vertical component of an
earthquake. The new code NCSE-94 specifies vertical accelerations equal to 70% of the
horizontal ones. The paper deals with the analysis of single layer and double layer
spatial structures under the seismic loads. Results are presented showing the importance
of the seismic vertical effects when compared with dead loads as well as life loads such
as wind and snow.
p.p. 453 - 461
Índice
7.02.- MODELIZACIÓN SIMPLIFICADA DE LA DEGRADACIÓN EN ESTRUCTURAS
Perera, R.; Carnicero, A.; Alarcón, E. y Flórez-López, J.
Numerous damage models have been developed in order to analise the
seismic behavior. Among the different possibilities existing in the literature, it is very
clear that models developed along the lines of Continuum Damage Mechanics are more
consistent with the definition of damage like a phenomenon with mechanical consecuences as
they include explicitly the coupling between damage and mechanical behaviour.
On de other hand, for seismic processes, phenomena such as low cicle
fatigue may have a pronounced effect on the overal behavior of thr frames and, therefore,
it´s consideration turns out to be very important. However, most of existing models
evaluate the damage only as a functionb of the maximum amplitude of cyclic deformation
with out considering the number of cycles. In this paper, it is proposed a simplified
model of evaluating the damage including the low cycle fatigue. Such model employs in its
formulation irreversible thermodynamics and internal state variable theory.
p.p. 463 - 469
Índice
7.03.- INFLUENCIA DE LAS CARACTERÍSTICAS ESTRUCTURALES DE LOS
PUENTES EN LA DETERMINACIÓN DE SU VULNERABILIDAD SÍSMICA
Maldonado, E.; Casas, J.R. y Canas, J.A.
Determining the seismic vulnerability of the bridge inventory of a city
is a quite mandatory need. Day by day the programs of attention post-earthquake force to
have the planning of the elements that involve their development. So, the highway systems
are an important aspect to consider and the bridges are important elements to account
inside the transportation systems. Because of all the above mentioned, the seismic
vulnerability studies of bridges are a topic of great interest currently. As a first
approach to develop seismic vulnerability studies of bridges, we have carried out the
current study of the bridges structural features in the determination of their seismic
vulnerability.
p.p. 471 - 479
Índice
7.04.- MÉTODOS DE ANÁLISIS SÍSMICO DE UN EDIFICIO CONTEMPLADOS
EN EL BORRADOR DEL EUROCÓDIGO
De la Fuente Martín, Pablo
The paper sets out the most important aspects of the structural
analysis of buildings included in the Eurocode 8, Part 1.2. Regarding the modal response
analysis, which is the standard method for this Eurocode 8, we examine modelling and
methods of analysis. As an example, we have made an analysis for a tall building subjected
to seismic adtivity. The modal response analysis was carried out with a spatial model and
two planar models. A simplified modal response spectrum analysis was also performed.
Finally we compare the results obtained from the various methods of analysis.
p.p. 481 - 490
Índice
7.05.- SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF AN OLD LIGHT-HOUSE UNDER STRONG GROUND
SHAKING
Sincraian, Gabriela; Sousa Oliveira, Carlos; Vieira de Lemos, J.
On the morning of July 9, 1998, the islands of Faial, Pico and São
Jorge in the archipel of the Azores were shaken by a md = 6 earthquake with
epicenter localized in the northern sector of the canal, which separates Pico from Faial.
The ground motion caused by this earthquake was recorded in a SMA-1 accelerograph located
at 15 km from the epicenter, with a PGA of 0.39 g.
Located at about 5 km from the epicenter, the light-house of
Ribeirinha, a masonry structure built around 1918, has undergone extense damage in the
tower, with relative displacements of 50 cm among stones. Using the discrete element
method, in a 3-D equilibrium, with rigid blocks separated by joints made of
elastic-plastic material, it was possible to reproduce approximately the same pattern of
deformation as observed in the prototype, for the case where the above record was scaled
by a factor of 2.
p.p. 491 - 502
Índice
7.06.- CÁLCULO SÍSMICO DE TANQUES DE GAS NATURAL LICUADO
Goicolea, José Mª; Gabaldón F.; Anero, R. y Gil Iriarte, R.
A procedure for seismic analysis of Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) tanks
is presented, together with its application to a tank currently under construction in
Cartagena (Spain). This tank has a double containment and a nominal capacity of 105.000 m3.
Due to safety considerations, these tanks require maximum reliability
in the calculations. Hence, a three stage modelling secuence has been adopted: 1 d.o.l.
models, 2D finite element models with beams elements, and 3D finite element models with
shell elements. The comparison of the results allow us to arrive to useful conclusions
regarding the use of each type of model and the quality of the results obtained. The
results of the study for sloshing wave height are also discussed. These are evaluated in
an overly conservative fashion by the code NCSE-94.
p.p. 503 - 511
Índice
7.07.- EFECTO DE LA NO LINEALIDAD GEOMÉTRICA SOBRE LAS PROPIEDADES
DINÁMICAS DE EDIFICACIONES APORTICADAS, DURANTE UN SISMO
Safina Melone, Salvador
The present work seeks, in a simple way, to estimate the influence
that has the effect of the geometric not lineality on the determination of the fundamental
dynamic properties of frame constructions, like consequence of recognizing the effect that
has the axial load on the rigidity rotational of the columns during the occurrence of an
earthquake. In particular, is presented the effect that has on the frequencies and modal
forms of vibration for regular building of concrete and steel of different relationships
of slenderness.
p.p. 513 - 521
Índice
7.08.- APROXIMACIÓN ESTÁTICA DEL ESTADO TENSIONAL EXISTENTE EN LA
SECCIÓN TRANSVERSAL DE UNA ESTRUCTURA ENTERRADA SOMETIDA A LA PROPAGACIÓN VERTICAL DE
LAS ONDAS "P" Y "S"
Gil Martín, L.M.; Hernández Montes, E. y De la Fuente Martín, P.
This paper presents a simplified static analysis method to approximate
the state of stress in a cross section of a buried structure. The cross section shape is
square and its dimensions are small. The structure is buried in a granular soil and the
thickness of the stratum is constant. The structure is excited by P and S vertical waves,
which have been introduced by vertical and horizontal statistically independents
accelerograms compatibles with the response spectra of Regulatory Guide 1.6. The static
model will be subjected to the free field displacements. These displacements will be
imposed to some nodes. The horizontal dimension of the model will be calculated using the
fundamental modes displacements.
p.p. 523 - 531
Índice
7.09.- COMPORTAMIENTO DE GASODUCTOS EN ÁREAS DE RIESGO SÍSMICO
Fdez. Loeches, R.; Lana, J.A.; Museros, P.; Retana, M.P. y Alarcón,
E.
Presently buried pipelines are the most reliable method for the
transportation of gas. Nevertheles, not much attention is paid to the seismic behaviour in
the design of gas pipelines, and seismic risk is not given in European Codes the
importance it surely deserves. In this paper two methods, which are proposed by the
American Society of Civil Engineering (ASCE) for the evaluation of the pipeline resistance
to fault displacements, are reviewed and compared. Two computer programs based on these
methods have been developed and their main features presented herein.
p.p. 533 - 541
Índice
7.10.- ANÁLISIS DE LA SEGURIDAD SÍSMICA DE LA PRESA DE ZORITA
Romera, Luís E. y Hernández, Santiago
A structural safety analysis of the Zorita Dam is presented. The set of
loads considered included hydrostatic pressure, thermal actions and the design earthquake
used in the construction of the nuclear power plant J. Cabrera, located nearby the dam.
The structure is separated into three main subsystems: the cross
section of dam in the buttress area, the floodgate and the upper footbridge. Each of them
is analysed separately considering the interaction with the remaining subsystems. Each
subsystem is analysed by mean of a finite elements model with different codes (EAGD-84 and
COSMOS/M), on account of the degree of adequation with the kind of problem to solve.
Changes in structural responses were evaluated under modifications on numerical values of
the mechanical parameters of the problem.
p.p. 543 - 552
Índice
7.11.- UTILIZACIÓN DE DISPOSITIVOS DE DISIPACIÓN EN PUENTES DE
GRAN LONGITUD
Astiz, M.A.; Muñoz-Rojas, J. y Fernández Troyano, L.
The design problems of long viaducts located in high seismicity
areas are analyzed in this paper. Longitudinal seismic effects are considered since they
transmit very important forces to the abutments of the bridge. The use of damping devices
is proposed as an economic and simple alternative to reduce these forces. Selection and
design criteria for damping devices are described in this paper taking also into account
thermal effects and erection methods. Methods of analysis which are based on complete or
simplified structural models are also described.
p.p. 553 - 561
Índice
7.12.- SIMULACIÓN PARAMÉTRICA DE ACELEROGRAMAS EN ESTUDIOS DE
VULNERABILIDAD SÍSMICA
Sánchez-Carratalá, Carlos R. y Martín, Manuel G.
This paper deals with univariate, one-dimensional numerical simulation
of accelerograms compatible with a prescribed power spectrum using autoregressive
moving-average models (ARMA), in the context of seismic vulnerability studies based on
damage indexes. Earthquake ground acceleration, that is modeled as a nonstationary
stochastic process with an evolutionary power spectrum, is generated from time series
corresponding to the associated stationary stochastic process, whose power is subsequently
modulated in the time domain. The determination of the ARMA model parameters is carried
out using the ACM fitting technique, based on an initial AR approach. The results obtained
with this technique for the modelling of the Kanai-Tajimi spectrum are presented and its
instability problems expounded.
p.p. 563 - 571
Índice
7.13.- IMPLEMENTACION EN ABAQUS DEL MODELO HISTERÉTICO DE DAÑO
CONSIDERANDO FATIGA DE BAJO CICLAJE PARA PORTICOS DE CONCRETO ARMADO
Picón Rodríguez, Ricardo A. y Flórez López, Julio
The CR structures should be capable of being accounted in the inelastic
range, by means of dissipation of energy through a stable hysteretic behavior. In this
paper it is presented an implementation of a damage model using ABAQUS, commercial soft
program which solves the global problem (nodal displacement of the structure). The finite
element was developed taking into account the Hysteretic Model of damage and Low Cycle
Fatigue which is based on the degradation mechanics, the continuum damage theory and
lumped plasticity models. SUPERDEG, algorithm that solves a local problem: numerical
calculation of loads and internal variables, in terms of displacements.
p.p. 573 - 581
Índice
7.14.- MODELO DE DAÑOS EN ELEMENTOS ESTRUCTURALES DE CONCRETO ARMADO
SOMETIDOS A FLEXO-COMPRESIÓN BIAXIAL
Marante, María E. y Flórez López, Julio
In this paper an approach is presented, based on the concepts of
mechanics fracture, continuum damage theory and lumped plasticity models which describes
the hysteretic behavior of a CR cantilever element subject to biaxial bending. The model
describes the structural damage in terms of the permanents generalized plastic
deformations, the stiffness and strength degradation. The element is considered as the
assemblage of an elastic beam-column and an inelastic hinge where is assumed to
concentrate the energy dissipation while the beam-column remains elastic. Seven internal
variables, which measure plastic rotations and the state of damage of the member, are
introduced. The accuracy of the model is calibrated by numerical simulations of
experiments found in the literature.
p.p. 583 - 591
Índice
8.- DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION (DISEÑO Y CONSTRUCCIÓN)
8.01.- VALORES DE DUCTILIDAD Y DESPLAZAMIENTOS DESARROLLADOS EN UN
EDIFICIO DE HºAº (ELS y ELU). ANALISIS TEMPORAL DE LA MIGRACION DE ROTULAS
Catalán Goñi, A. y Bozzo Rotondo, L.
Codes and standards have a classification of the seismic load level
and response associated to an structure and its location. The response is associated to
the acceptable damage limit state for the resisting structure as well as for the
non-intentional structural elements. In general, the levels (earthquake - damage) are
qualitatively defined although there is not a clear quantitative definition. The damage is
defined after the level of loading is established.
An objective design (a design with a variety of states) indicates the
necessity of incorporating in the numeric stage new concepts such as energy and damage
index, among others. In this work the nonlinear response of a built structured is analyzed
based on the serviceability limit state (ELF -p= building life period) and the ultimate
limit state (ELU - p = 500 years). An approximate methodology to defined the loading for
each limit state is proposed and it is demonstrated that the code-designed building do not
satisfies the necessary conditions for a good seismic design.
p.p. 595 - 607
Índice
8.02.- UNIONES VIGA-COLUMNA DÚCTILES PARA RESISTENCIA SÍSMICA. EL
TERREMOTO DE NORTHRIDGE
Gil, L.M.; Hernández, E. y Bayo, E.
In order to avoid a collapse in a steel structure during an earthquake
we have to warranty a good steel design. The structure have to be able to dissipate a
quantity of energy in its connections. Steel rigid frames are supposed to dissipate the
main part of the energy in its plastics hinges, which are develops in some of its
connections.
Many brittle fractures appeared in connections during Northridge
earthquake, and these connections did not develop any plastic hinge. This paper propose
some procedures to warranty the ductility of some connections, for new and built frames.
p.p. 609 - 618
Índice
8.03.- VARIABILIDAD DEL PERIODO
PROPIO DE LOS EDIFICIOS DE HORMIGÓN ARMADO SEGÚN SUS CARACTERÍSTICAS CONSTRUCTIVAS
Caselles, J.O.; Espinoza, F.; Muñoz, F.; Lana, X; Sánchez, J.;
Navarro, M.; Chourak, M. y De La Cruz, S.T.
Recently, some experimental studies about the relationship of the
natural period and height of buildings have been developed in Spain. The great variability
of this period is done by a lot of variables, as from structural elements as
non-structural ones, that are usually not taken into account because are assumed to be not
important or to have a small variation in a standard construction.
To study the importance that these variables could be, the main period
of 20 buildings of Barcelona and Adra (Almería) with 4 floors has been measured. This
buildings are houses and schools with available structural plans and represent different
structural designs. In this work we present the results of a multivariable regression of
the fundamental period versus 11 variables that has been take into account.
p.p. 619 - 624
Índice
8.04.- COMPORTAMIENTO SÍSMICO
DE LOS PUENTES METÁLICOS. LOS TERREMOTOS DE NORTHRIDGE Y KOBE
Hernández, E.; Gil, L.M.; Bayo, E. y Rúa, E.
Northridge and Kobe earthquakes (California –1994- and Kobe bay
–1995-) are the most destructives ones in the history of USA and Japan, respectively.
Japanish and American seismic codes are of the most advanced all over the world, anyway,
both earthquakes were very destructives and in there areas many damages arose. Steel
bridges in Kobe area were specially affected and many type of damages were displayed. In
this paper an analysis of the most common damages in steel bridges is presented, also,
some interesting points of Japanish seismic code are commented.
p.p. 625 - 633
Índice
8.05.- APLICACIÓN DEL CONTROL DE ESTRUCTURAS AL DISEÑO ANTISÍSMICO
López Almansa, F
The objective of this paper is a state-of-the-art review of the
control of vibrations of civil engineering structures generated by seismic motions. The
paper is organised as follows: (1) seismic design is divided into traditional and
innovative solutions (control techniques); (2) a classification of control systems into
passive, active, semi-active and hybrid is presented; (3) passive systems are grouped in
three general categories: base (seismic) isolation, energy dissipators and mass dampers
and (4) main proposed technologies and their applications are described. Some global
conclusions and remarks are discussed to highlight the scope and feasibility of these
techniques.
p.p. 635 - 644
Índice
8.06.- EVALUACIÓN DE LOS EFECTOS DE LA DUCTILIDAD EN LA RESPUESTA
SÍSMICA DE ESTRUCTURAS
Ordóñez V., Arturo
General commentaries related to the use of Design Response Spectro
including the reduction capacity factors R, are briefly stated. Including the performance
under real earthquakes.The importance of evaluating nonductil elements in the seismic
load-path, for the real R factors associated to the final capacity of the main systems is
recomended.
p.p. 645 - 652
Índice
8.07.- CALIFICACIÓN SÍSMICA BASADA EN LA EXPERIENCIA
Beltrán, Francisco
The paper presents the key elements of the methodology for seismic
qualification of equipment based on the experience about the effects of actual
earthquakes. The methodology is based on the concept of successive screening. Four
screening evaluations are defined. Firstly, the demand imposed by the design earthquake is
compared with the capacity of same class equipment derived from the experience. In the
second screen, the similarity of the component to those included in the experience
database is verified and some caveats for good performance are checked. Finally, the
capacity of the anchorage is evaluated and the absence of potential spatial interaction is
assessd.
p.p. 653 - 661
Índice
8.08.- METODOLOGÍA PARA LA CALIFICACIÓN SÍSMICA DE COMPONENTES
ELÉCTRICOS INSTALADOS EN CENTRALES
González, P.; Blöbaum, A.; López, M.; Zapico, J.L.; Fernández, A.
y Molina, F.J.
By the growing interest in the
security of people and the environment it has come to pay more attention to that the
instruments which are used in central power plants and that they are working perfect. In
the power plants, when equipment are installed, it can be propose a methodology to verify
correct behaviour. The objective is to validate this methodology. For that it had be
designed an investigation program. This program should prove the viability of this
methodology and his precision by the comparison with seismic tests on equipment.
p.p. 663 - 671
Índice
8.09.- MEJORA DEL COMPORTAMIENTO SISMORRESISTENTE DE LAS
EDIFICIACIONES POR INCORPORACIÓN DE PANTALLAS CONTINÚAS DE RIGIDIZACIÓN AL GLOBAL DE LA
ESTRUCTURA
Vallecillo Capilla A., Osuna Barrero J.M., Hernández Cortés E.
After the analysis of the damages caused in different
constructions, located in different geographical zones, as consequence of seismic
movements. It has been accomplished a comparison between those which were having rigid
screens and those which not.
Studied we result them we arrive to conclusions that permit us to
assert the kindness of its utilisation and the criteria that define the design of the same
for its better form of work.
p.p. 673 - 681
Índice
8.10.- STRATEGIES TO ENLARGE
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD MITIGATION IN MACEDONIA
Timiovska, Lenka S.
We can mark the limits of earthquake-hazard mitigation from the very
broad, which include any type of action taken prior to an earthquake to decrease its
effects, to the very narrow, which contain specific actions to design, and retrofit
structures to minimize earthquake damage. Nevertheless, to define smaller used and more
effective mitigation as those actions that smaller impacts of earthquakes through
controlling the quality and location of buildings and other structures. These are
strategies that lessen the expected losses. They would be acceptable through land-use
regulations, building codes, building and design practices, sitting structures,
retrofitting buildings, and securing objects within buildings.
p.p. 683 - 688
Índice
8.11.- DISEÑO DE UN FORJADO SISMORRESISTENTE DE HORMIGÓN ARMADO,
CON JÁCENAS BIDIRECCIONALES DESCOLGADAS, CONSTRUIDO CON ENCOFRADOS CONTINUOS
Osuna Barrero J.M., Vallecillo Capilla A., Hernández Cortés E.
From the moment of the entry into
force in Spain of the new Norm Sismorresistent NCSE-94, the technical personnel that were
designing and were calculating the structures have had to apply new constructive criteria
in its conception. In high seismic risk zones with an important seismic degree, is
proscribeed the utilization of industrious constructive solutions until later. Such is the
case of the fixed beam, forbidden for built structures in places with ac ³ 0,16·g.
p.p. 689 - 700
Índice
8.12.- EARTHQUAKE MONITORING AND MITIGATION IN MACEDONIA
Timiovska, Lenka S.
Earthquake monitoring programs require substantial information on the
hazard through improved a national seismological networks. The important indicator to show
expected earthquake hazard is the distribution and the rate of earthquakes occurrence in
the past. Especially, for our country we use historical records for obtained the following
maps in the seismic monitoring: map of source zones (seismogenic zone maps), map of
maximum seismic intensities Imax which indicates the source generating these
earthquakes, map of intensities depend on ground conditions. As is known such prediction
based on seismic gaps is needed to formulate appropriate earthquake disaster mitigation
measures.
p.p. 701 - 703
Índice
9.- EXPERIMENTAL ANALISYS (ESTUDIOS EXPERIMENTALES)
9.01.- ENSAYOS PSEUDODINÁMICOS A CORTANTE EN MUROS DE HORMIGÓN
ARMADO. EVOLUCIÓN DE LA FRECUENCIA Y EL AMORTIGUAMIENTO DURANTE EL TERREMOTO
Molina, F.J.; Verzeletti, G.; Pegon, P.; Magonette, G.; Tognoli,
P.; Saldarini, G. y Tirelli, D.
Several specimens of reinforced-concrete walls have been seismically
tested in shear. The specimens presented different amount of reinforcement, different
initial eigenfrequency or different normal load. Every specimen was submitted to the
action of a horizontal accelerogram, with successive growing amplitudes, using the
pseudodynamic method. A first analysis of the results allows to know the evolution of the
eigenfrequency and damping ratio during the earthquakes thanks to an identification method
working in the time domain. Since those parameters are in fact able to give a reliable
prediction of the response by just entering in the response spectrum, they have a great
value for the design of this type of structures.
p.p. 707 - 715
Índice
9.02.- MODELADO A PEQUEÑA ESCALA Y ENSAYO SÍSMICO DE UN PUENTE
IRREGULAR
Zapico, J.L.; Molina, F.J.; Taylor, C.A. y Crewe, A.
This paper describes the technique which allowed the successful
execution of the seismic shaking-table test of a bridge with a 1:50 scale. The similarity
laws, the materials and the mechanical design were adopted in such a way to allow the
reproduction of the elastic stiffness and the yielding limit corresponding to the
prototype. That prototype consisted of an irregular reinforced concrete bridge designed
according to Eurocode 8. The test complemented other tests with the real materials at
1:2.5 scale, which served the assessment of the security level of said design. The
obtained results, relating maximum values for the small-scale model, were in good
correlation with those of the large-scale model, although the measured forces were not so
reliable as the displacements in the non-linear phase.
p.p. 717 - 726
Índice
9.03.- PROYECTO DE ESTRUCTURAS SISMORRESISTENTES UTILIZANDO DOS
NUEVOS DISIPADORES DE ENERGÍA DE TIPO HISTERÉTICO
Benavent Climent, Amadeo y Akiyama, Hirishi
In this paper, an earthquake-resistant structure is proposed which
consists of a conventional bare frame designed for sustaining only the gravitational
loads, and two new energy dissipators developed by the authors. Design criteria and simple
formulas for predicting the seismic response of the structure are provided.
Finally, for illustrating purposes, a frame equipped with the new
energy dissipators is designed and compared with the conventional frame designed according
the spanish seismic code NCSE-94. as a result, it is shown that the frame with the new
energy dissipators is cheaper and exhibits a better seismic performance than the
conventional moment resisting bare frame.
p.p. 727 - 736
Índice
9.04.- DETERMINACION DE LA POSICION Y GEOMETRIA DE CAVIDADES EN
SUELOS MEDIANTE APLICACION DE CARGAS DINAMICAS EN LA SUPERFICIE
Suárez J. y Gallego R.
In this communication, a boundary integral approach proposed by the
authors for the solution of inverse identification problems for harmonic elastodynamic
antiplane states, to find the position and geometry of cavities in soils, is presented.
The soil is modeled as a homogeneous, elastic, isotropic halfspace, and dynamic loads are
applied in the surface. The procedure is based on the boundary integral equation for the
variations, which is obtained appliying variational calculus, by considering twice the
direct problem: firstly with the real geometry of the flaw, and secondly with the assumed
geometry. Using standard discretization techniques in the boundary element method, the
integral equation is transformed is a set of algebraical equations, which are solved by
the weighted least squares method, computing the value of the variations of the geometry
which approach the assumed geometry to the real one. Through an iterative algorithm the
computed geometry can be superpossed to the real one.
p.p. 737 - 745
Índice
9.05.- SIMULATED LONG LIFE TESTS FOR RAILWAY EQUIPMENT, DEFINED BY
AUTO SPECTRAL DENSITY FUNCTIONS OF ACCELERATION. STATITICAL AND NUMERICAL PROBLEMS
García Ruiz, Paloma y Navarro Colóm, Francisco
The modern specifications for Long Life Vibration tests define the
action by the auto spectral density functions of acceleration, in control points normally
coincident with fixing points of equipment. In time dominium, the signal is aleatoric and
stacionary, with normal distribution and time duration specified by test. The practical
application of that definition in numerical contyrolled equipment has caracteristics
problems:
- Number of armonic components, and time of vibration signal. Number of
statistical degrees of freedom.
- Generation of a aleatoric signal by armonics, with real aleatoric
fases
- Iterative compensation of dynamic coupling specimen-seismic simulator
p.p. 747
Índice
9.06.- EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC PARAMETERS OF BRIDGE
SUPPORTS IN NEOPRENE
Navarro Colóm, Francisco y Nistorescu, Daniel
Neoprene supports supose a low rigidity component in the structure of a
bridge, and has a fundamental influence in the dynamic response of the total structure. In
this paper we describe the dynamic test for diferent specimens of supports. The studied
parameters are:
- Vertical compression
- Frecuency of senoidal signal fo shear stress
- Dimension of support, and composition
- Maximum deformation
The results are:
- Transverasl shear modulus
- Hysteretic damping and energetic dissipation
- Fatigue
p.p. 749
Índice
9.07.- CUANTIFICACIÓN DEL ANÁLISIS PSEUDOESPECTRAL, USANDO LA
INTEGRAL DE DUHAMEL EXACTA
Villegas González, Ower A. y Sánchez Cabañero, J.G.
Given an accelerogram input, the pseudospectra approach normally is
computed in order to obtain a fast response to be used on the calculations. The present
paper carry out a comparison between the exact and approximated results calculated with
the spectra and quantify the differences. According to the type and properties of the
functions involved and their properties, some mathematical tools are used on the analysis.
Assuming we have specify bounded continous family of linear operator L(t),
with t Î R, acting on an normed linear space of A-valued
functions b (x). Suppose that m: b (R) ® A, is A-valued
idempotent s - additive bounded measure and j t (x), y t, s
(x) and f t (x) are A-valued
functions Ì b (x) are
continous in t Î R.
If the operators L(t) retain separability of the range
values then,
ò o L (t
) Y t , s m dt and ò o L (t ) j t m dt
have finite values bounded values possible evaluate explicity in order
to compare with the pseudoespectral approach.
p.p. 751 - 756
Índice
|